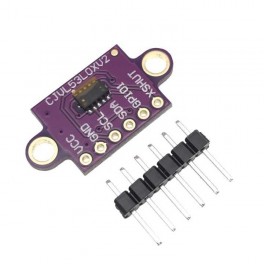
Descriptions:
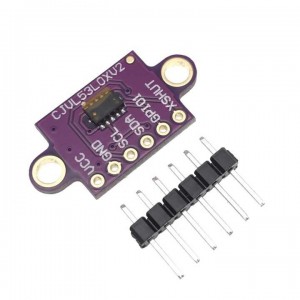
The VL53L0X from ST Microelectronics is a time-of-flight ranging
system integrated into a compact module. This board is a carrier for
the VL53L0X, so we recommend careful reading of the VL53L0X
datasheet (1MB pdf) before using this product.
The VL53L0 uses ST’s FlightSense technology to precisely
measure how long it takes for emitted pulses of infrared laser
light to reach the nearest object and be reflected back to a
detector, so it can be considered a tiny, self-contained lidar system.
This time-of-flight (TOF) measurement enables it to accurately
determine the absolute distance to a target without the object’s
reflectance greatly influencing the measurement. The sensor can
report distances of up to 2 m (6.6 ft) with 1 mm resolution, but its
effective range and accuracy (noise) depend heavily on ambient conditions
and target characteristics like reflectance and size, as well as the sensor
configuration. (The sensor’s accuracy is specified to range from ±3% at best
to over ±10% in less optimal conditions.)
Ranging measurements are available through the sensor’s I²C (TWI) interface,
which is also used to configure sensor settings, and the sensor provides two
additional pins: a shutdown input and an interrupt output.
The VL53L0X is a great IC, but its small, leadless, LGA package makes it
difficult for the typical student or hobbyist to use. It also operates at a
recommended voltage of 2.8 V, which can make interfacing difficult for
microcontrollers operating at 3.3 V or 5 V. Our breakout board addresses
these issues, making it easier to get started using the sensor, while
keeping the overall size as small as possible.
PIN Description
VDD Regulated 2.8 V output. Almost 150 mA is available to power
external components. (If you want to bypass the internal regulator,
you can instead use this pin as a 2.8 V input with VIN disconnected.)
VIN This is the main 2.6 V to 5.5 V power supply connection.
The SCL and SDA level shifters pull the I²C lines high to this level.
GND The ground (0 V) connection for your power supply.
Your I²C control source must also share a common ground with this board.
SDA Level-shifted I²C data line: HIGH is VIN, LOW is 0 V
SCL Level-shifted I²C clock line: HIGH is VIN, LOW is 0 V
XSHUT This pin is an active-low shutdown input; the board
pulls it up to VDD to enable the sensor by default. Driving this pin low
puts the sensor into hardware standby. This input is not level-shifted.
 Maximize
Maximize